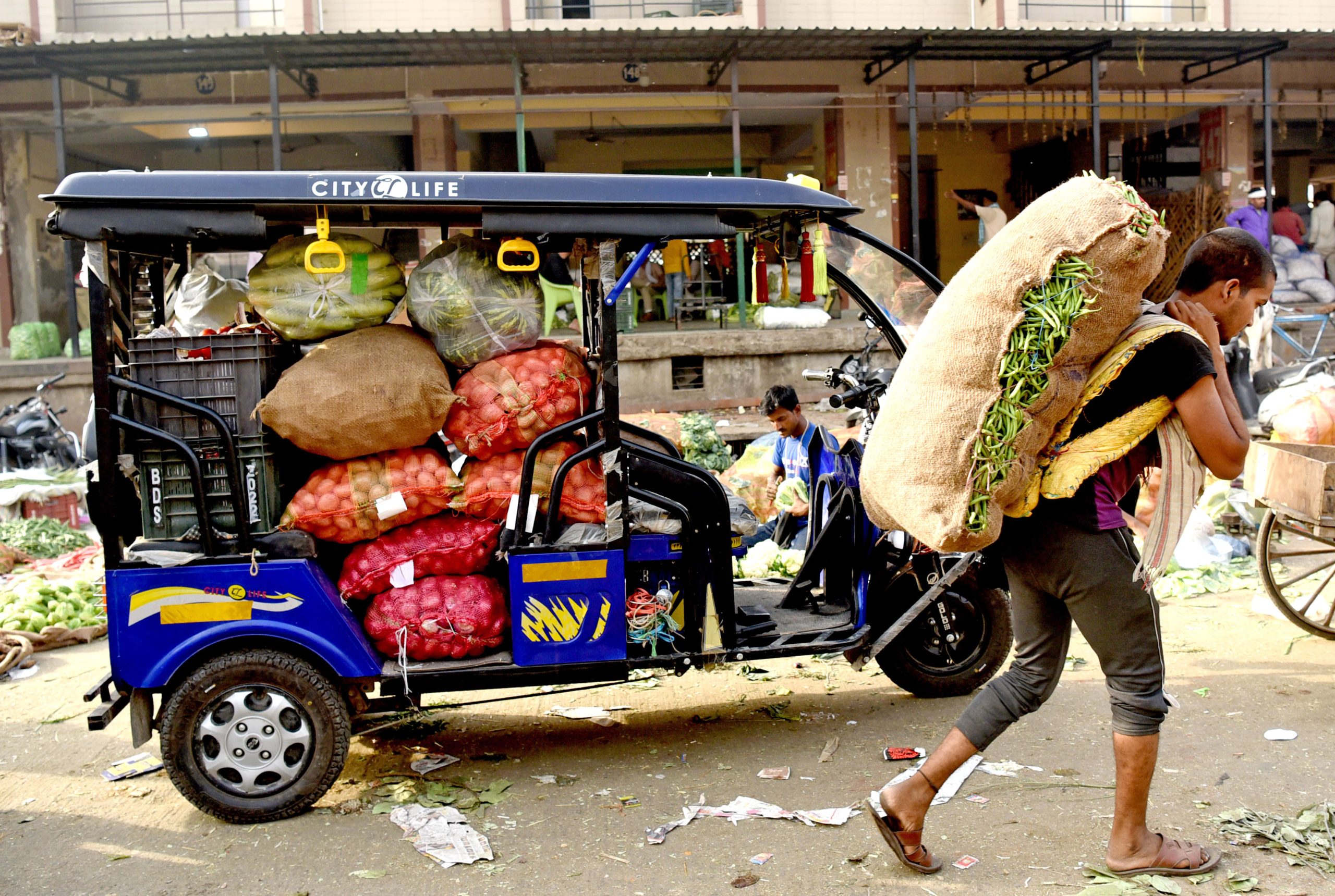
Maharashtra has emerged as the leading beneficiary under the Cold Chain scheme of the Pradhan Mantri Kisan Sampada Yojana (PMKSY), receiving grants-in-aid totaling ₹431.62 crore. This makes it the top recipient, followed by Uttarakhand and Andhra Pradesh, which received ₹255.57 crore and ₹213.97 crore, respectively, as per the Ministry of Food Processing Industries.
Since its inception in 2008, the Integrated Cold Chain and Value Addition Infrastructure scheme under PMKSY has approved 399 projects, with 284 already operational.
The initiative aims to strengthen India’s agricultural supply chain by minimizing post-harvest losses and promoting value addition to agricultural produce.
The scheme operates on a demand-driven basis, with the Ministry periodically inviting proposals through Expressions of Interest (EoIs). These are published on the Ministry’s website and circulated via press releases and newspapers. Eligible applicants include small farmers, Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs), NGOs, Public Sector Undertakings (PSUs), and private enterprises.
To date, the scheme has disbursed ₹2,366.85 crore, enabling the establishment of robust cold chain infrastructure, even in remote areas.
Initially launched as the Scheme for Agro-Marine Processing and Development of Agro-Processing Clusters (SAMPADA) in May 2017, the initiative was later rebranded as PM Kisan Sampada Yojana. Allocated ₹6,000 crore for the 2016-2020 period, the scheme was designed to modernize infrastructure and establish efficient supply chains from farms to retail outlets.
The scheme’s objectives include boosting the growth of the food processing sector, improving returns for farmers, reducing agricultural wastage, and increasing the level of food processing and exports.
PMKSY is structured around seven key components, each targeting specific areas of development within the food processing ecosystem.
These include Mega Food Parks, Integrated Cold Chain and Value Addition Infrastructure, Infrastructure for Agro-Processing Clusters, Creation of Backward and Forward Linkages, Creation/Expansion of Food Processing and Preservation Capacities, Food Safety and Quality Assurance Infrastructure, and Human Resources and Institutions.