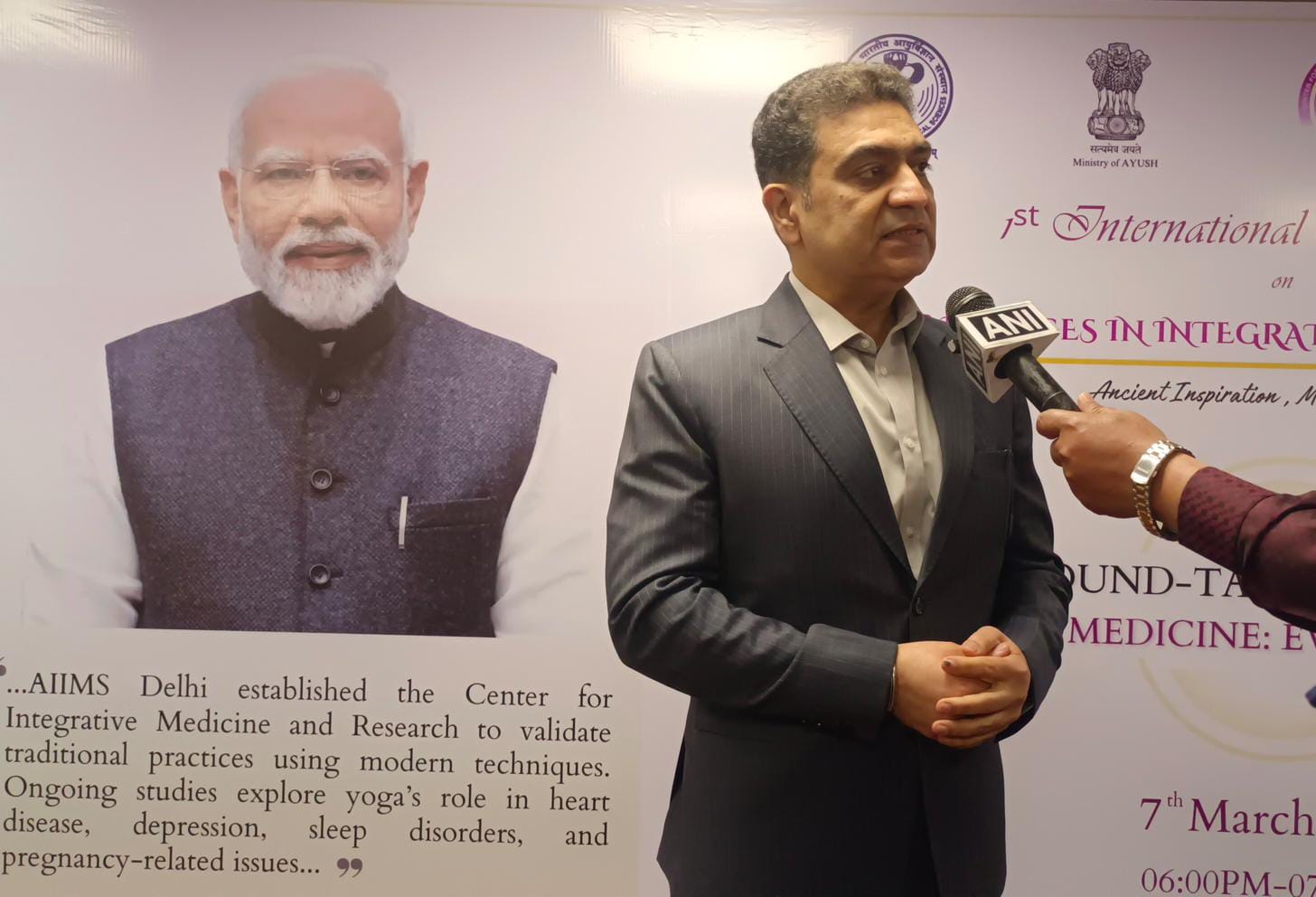
The Centre for Integrative Medicine and Research (CIMR) at AIIMS, New Delhi, is hosting its first international conference on ‘Advances in Integrative Medicine.’ This two-day event has convened experts from around the world to examine the synergy between traditional healing practices and modern medical science for improved healthcare outcomes. Since its establishment in 2016, CIMR has been a leading institution in integrative medicine research, particularly in validating the efficacy of yoga as a therapeutic intervention for neurological and cardiac conditions.
The conference focuses on the increasing acceptance of yoga as a credible and cost-effective therapy for neurological and cardiac conditions. Over the past eight years, CIMR has collaborated with 20 departments at AIIMS, conducting extensive research on the medical benefits of yoga. Their studies have been published in leading scientific journals, drawing interest from global medical communities.
During the conference, Dr. Gautam Sharma, Founder Professor in-charge of CIMR, shared significant findings on yoga’s health benefits. According to CIMR’s research, yoga has been scientifically proven to ease migraines, reduce episodes of syncope (temporary loss of consciousness due to a drop in blood pressure), and support heart health.
Dr. Sharma stated that their studies show yoga’s effectiveness as an add-on therapy, improving patients’ quality of life. Speaking with DD News, he explained, “We found that yoga reduced the severity of migraines in patients and significantly decreased syncope episodes in individuals who practiced yoga regularly.”
CIMR’s research has received recognition from prestigious global scientific organisations. Dr. Sharma was invited by the European Society of Cardiology to present CIMR’s findings on yoga’s role as a therapeutic intervention. Additionally, the American Heart Rhythm Society and the European Society of Cardiology have expressed keen interest in exploring yoga-based treatments further.
One of CIMR’s studies focused on the economic burden of vaso-vagal syncope, a condition where a sudden drop in heart rate and blood pressure leads to fainting. A past study from the United States estimated that approximately 740,000 emergency visits and 460,000 hospital admissions occur annually due to vaso-vagal syncope, resulting in high financial costs.
CIMR’s research found that integrating yoga into treatment plans significantly reduced the occurrence of syncopal and pre-syncopal events. When combined with medical treatment, yoga proved to be more effective than medication alone. This suggests that yoga could serve as a cost-effective and safe alternative for managing syncope, potentially lowering the financial burden on healthcare systems.
CIMR’s research underscores the potential of yoga as a valuable addition to conventional medical treatments, particularly in managing syncope and other neurological and cardiac conditions. By integrating yoga into treatment plans, healthcare providers can offer a cost-effective, safe, and scientifically supported therapy that enhances patient outcomes. The first international conference on integrative medicine at AIIMS represents a pivotal moment in advancing holistic healthcare, fostering collaboration between traditional and modern medical sciences. With increasing global recognition and scientific validation, yoga is steadily emerging as a key component of contemporary healthcare, paving the way for a more integrative and patient-centered approach to medicine.